Triad inversions
Music theory can be intimidating, especially if you’re self-taught. In this guide, we look at some of the fundamentals that all songwriters should understand.
Learn more about Basic Music Theory in part 2 of this article.
In the age of the internet, a new wave of talent has entered the music industry—self-taught musicians. Online resources make it possible to learn the craft without a formal education, or even a without strong musical foundation in the first place.
The increased accessibility to recording software and the opportunity to spread music online has made it possible for DIY musicians to succeed without much (if any) prior musical experience. This is great for the music community, but artists can be even more effective with some knowledge of basic music theory.
In this article, we’ll cover the fundamentals. We’ll be covering rhythm, keys and chords, and chord progressions.
Don’t worry if you have zero experience with music theory; this discussion will be geared toward the fundamentals. You may vaguely know some of these concepts, but knowing their names will help to understand them further.
And if you have some experience with music theory, hopefully this article can help you brush up on your knowledge. Staying sharp with this stuff is like practicing anything else.
Rhythm, time signatures, and groove
Rhythm
They say that music is based on three things: rhythm, rhythm, and rhythm. And this isn’t an exaggeration! Put simply, rhythm is the placement of sounds in time, or simply “when sounds happen.” This is the foundation of all percussion and melody.
Some of the earliest musical traditions involved rhythmic-based group playing. Vocal shouts and percussion have been used in ceremony and celebration for thousands of years.
Time signatures
Time signatures simply describe the length of a measure. Measures are the basic building blocks of time in a piece of music. They determine structure, section lengths, and phrasing for melody, harmony, and rhythm.

Measure
If you’re producing music, you’re probably comfortable with the concept of the beat or “pulse” of a song—where you’re nodding your head. The time signature describes how those beats are felt and notated.
Time signature is described as a fraction. The bottom number (the denominator) says what type of note counts as a “beat.” Divide one by this number to get the length of this beat.
A 4 would mean the beat is a quarter note long, an 8 would give an eighth note, a 16 a sixteenth, and so on.
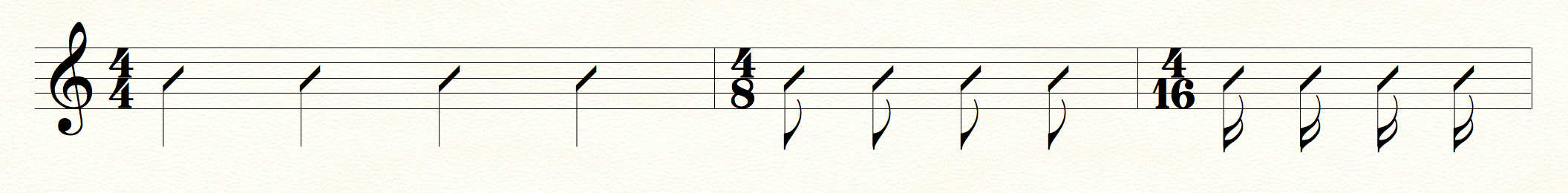
Time signature (denominator)
The top number (the numerator) shows how many of these beats fit into one measure.

Time signature (numerator)
The measures in DAWs (“digital audio workstations,” software like Ableton and Logic Pro) are essentially the same as in the notation above.

Ableton Live measures

Logic Pro measures
Most contemporary popular music is in 4/4 time. The 4 on bottom says that one beat is a quarter note, and the 4 on the top says that there are four quarter notes per measure.
4/4 time
You might be thinking, wouldn’t 4/4 and 2/2 (for example) be the same? Four quarter note should be the same as two half notes, right?

4/4 time vs. 2/2 time
Technically, a measure in each time signature would last the same amount of time at the same tempo. Often, composers will choose one or the other to simplify notation. But because the rhythm in 2/2 is grouped differently, the feel and phrasing can be different between the two.
2/2 will neatly group “events” (notes, percussion, etc.) into two sections per measure and create the feeling that there are two pulses per measure. This has an effect on the timing of chord changes and the phrasing of melodies.
4/4 time will more clearly outline four distinct pulses, allowing for more flexibility in the phrasing of ideas.
Here are some examples of less common time signatures in music you may have heard:
“Happy Birthday” (in 3/4)
“Mission Impossible Theme” (starts in 5/8, goes to 4/4 at 0:19)
OutKast - “Hey Ya!” (all in 4/4, with interspersed bars of 6/4 in the "Shake it like a Poloroid picture" section, from 4:01–4:03, 4:09–4:11, 4:17–4:19, and 4:26–4:28)
For the majority of those reading this, you’ll probably be using a decent amount of 4/4 time. By all means it’s fun to try out interesting time signatures, but many musical genres use mostly 4/4 so it’s a good idea to master this.
Understanding the standard is important. This will give you the tools to intentionally and creatively break away from it when you’d like.
Groove
The words “groove” and “rhythm” are often used in the same way. Here, we’re using “groove” to describe the feel of a rhythm. This simply comes from where the composer actually decided to place things in time.
Check out the three audio samples below. These are all in 4/4 time, but the placement of the snare drum drastically changes the feel of the drum part. It does this by emphasizing a certain beat in the measure, making it felt more powerfully.
Because of this, the snare determines where the listener will hear one of the stronger pulses.
The snare drum in most Western contemporary music acts as the backbeat. This serves as a response to the strongest beats, notably the downbeat (first beat) of a measure. In 4/4, the strongest beats are one and three and the backbeat is usually placed on beats two and four.
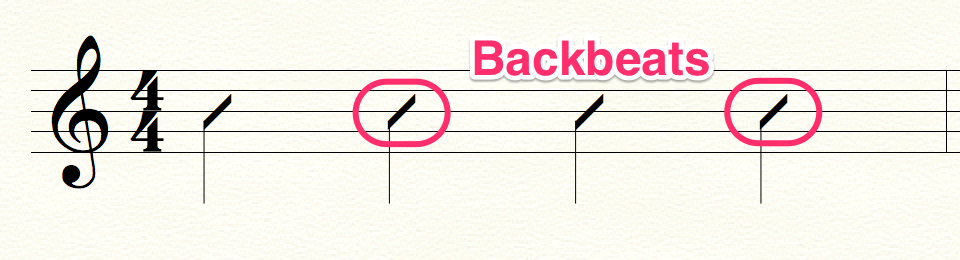
Backbeats
Keys, chords, and progressions
Keys
In most music, the key is the basis of all harmony and melody. Simply, a key is a collection of available notes.
Generally, the key determines which notes will sound harmonious in a piece of music—which ones sound “right." Musical traditions like rock, blues, and jazz also occasionally use notes from outside the key for embellishment and connecting notes within the key.
Keys are usually described in scales, which are “rooted” on a certain note and continue upward until reaching the same note an octave up. A scale’s notes are determined by certain distances between the notes. These are called intervals.
The main intervals used in Western music when developing scales are half steps (one step in a DAW) and whole steps (two steps in a DAW).
Western music generally uses a tuning system called “equal temperament," which has 12 half steps in an octave.

Equal temperament
There are two main types of keys you should understand—major and minor keys. The classic description of the major key is that it sounds “happy." The minor key, on the other hand, is said to sound “sad."
The notes of the major key are determined like this: root, whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, whole step, half step (1 octave above the root).
In the diagrams below, whole steps are denoted as “W” and half steps are denoted as “H.”
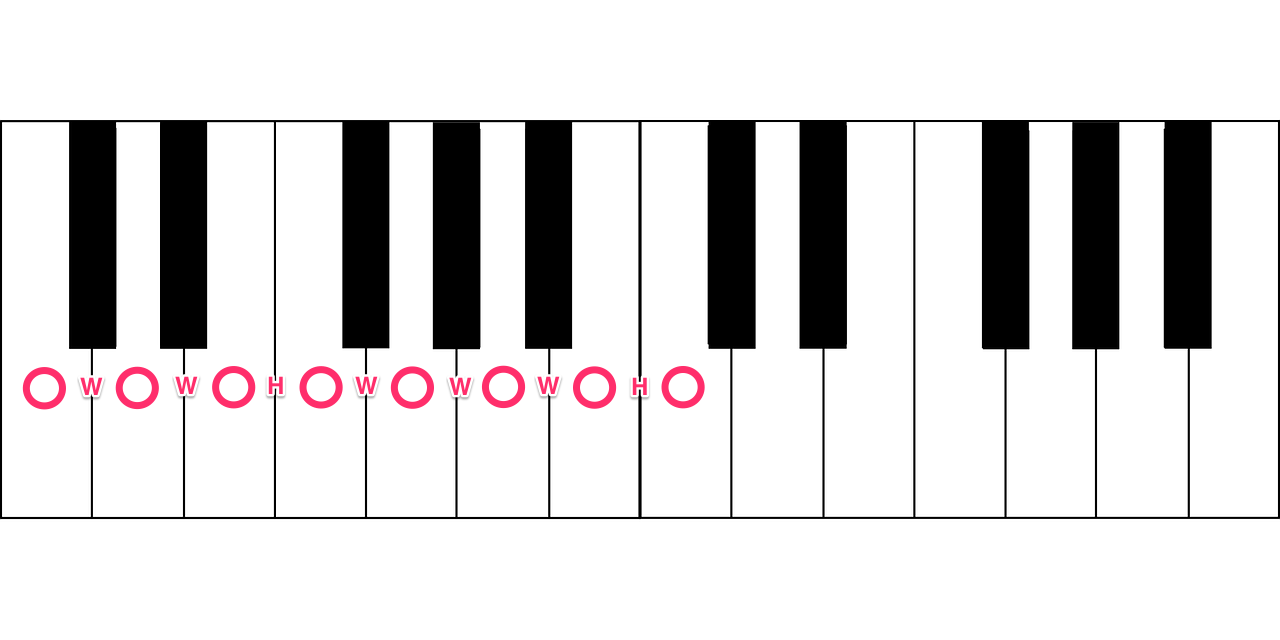
Major triad
The notes of the natural minor key are determined like this: root, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step (1 octave above the root). There are actually two more types of minor keys, but this is the main one worth knowing.
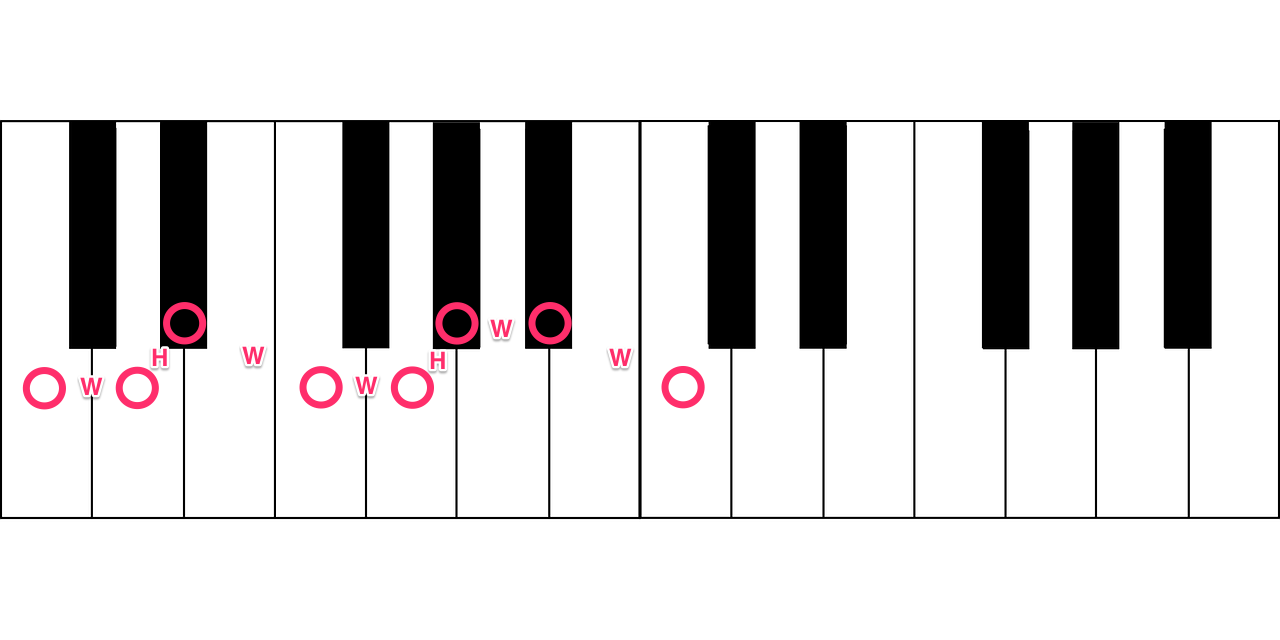
Minor scale
Scales can also be described using intervals in relationship to the root note. Notes are labeled based on their distance from the root. Generally, these are the names used for intervals at specific lengths:
- 0 steps = unison
- 1 step = minor second (half step)
- 2 steps = major second (whole step)
- 3 steps = minor third
- 4 steps = major third
- 5 steps = perfect fourth
- 6 steps = tritone
- 7 steps = perfect fifth
- 8 steps = minor sixth
- 9 steps = major sixth
- 10 steps = minor seventh
- 11 steps = major seventh
- 12 steps = octave
Note that fourths and fifths are called “perfect." This is because they are perfect intervals, which sound harmonious in both major and minor keys. See that both the C Major and C Minor scales above include F and G, which are the perfect fourth and fifth above C.
The unison (the same note played simultaneously, like in separate instruments) and the octave are also perfect intervals.
The tritone gets its name because it is three whole steps stacked on top of each other. It is one of the more “dissonant” intervals, meaning it creates tension that leads to a more “consonant” (or harmonious) sound.
The seven notes of the major scale would be the root note, a major second, major third, perfect fourth, perfect fifth, major sixth, and major seventh.

Major scale (by intervals)
The seven notes of the minor scale would be the root note, a major second, minor third, perfect fourth, perfect fifth, minor sixth, and minor seventh.

Minor scale (by intervals)
You may also hear notes just referred to by number. Minor intervals are usually referred to as “flats." The natural minor scale, for example, could be described as: “one, two, flat three, four, five, flat six, flat seven, one."
Scales are related to each other through the concept of modes. We won’t go too deep into modes in this article, but the idea is that starting a scale on a different note other than the root creates a different scale.
For example, if you play a C Major scale (all the white notes on a keyboard) from A to A, this is the A Natural Minor scale. In fact, playing any major scale starting on the sixth note of that major scale creates a natural minor scale, called the “related minor key."
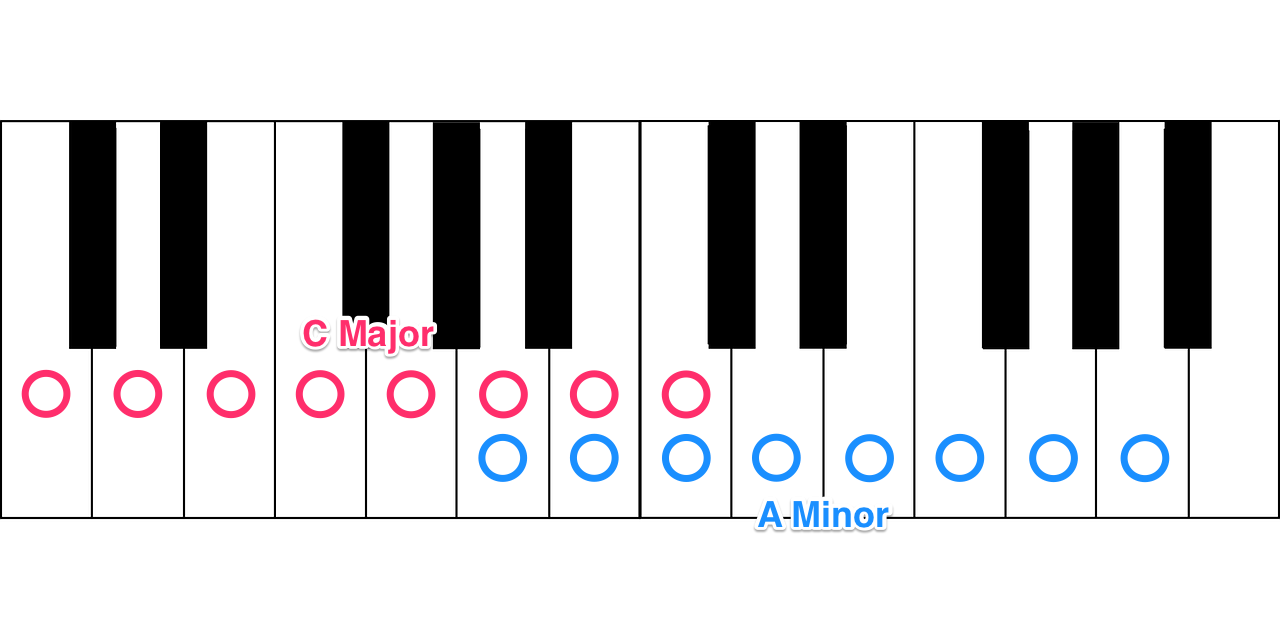
Related minor keys
If you’re able to play an instrument, learning how to play scales can be very useful. This makes them much easier to memorize and much easier to recall when working.
And you don’t have to be a virtuoso instrumentalist for this to help. The ability to play an instrument will make music theory more “real” for you and much less abstract.
Chords
A chord is a collection of three or more notes played simultaneously. In composition, different chords can be played consecutively (a progression—we’ll get to that next) to move the piece along.
Each chord in the sequence sustains for a certain amount of time, locking the measure(s) on that chord. Melodies can be built from the current chord.
Chords are generally built by adding non-adjacent notes from a scale. The number of notes we include in the chord determines its sound and how we notate it.
Triads
Stacking three non-adjacent notes from a scale creates a triad. This is the most basic type of chord, as the root, third, and fifth are enough information for our ears to identify a certain chord.
In the key of C Major, we could start at C (first note of the scale) and add E (third note of the scale) and G (fifth note of the scale) to create a C Major triad.
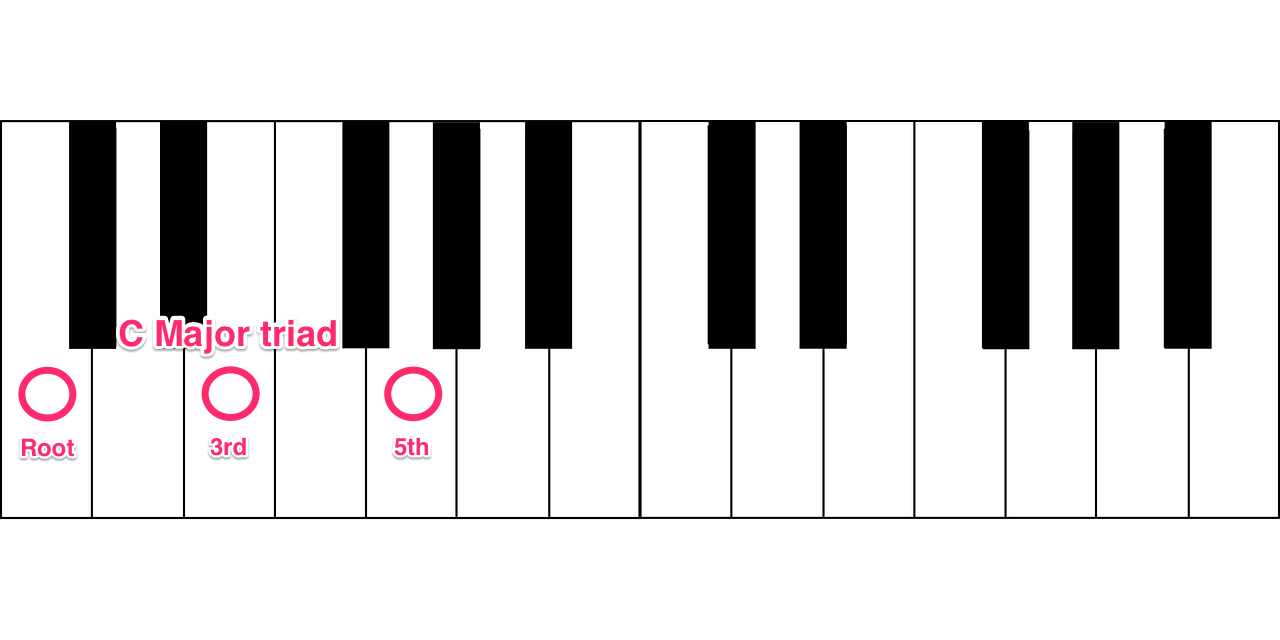
Major triad
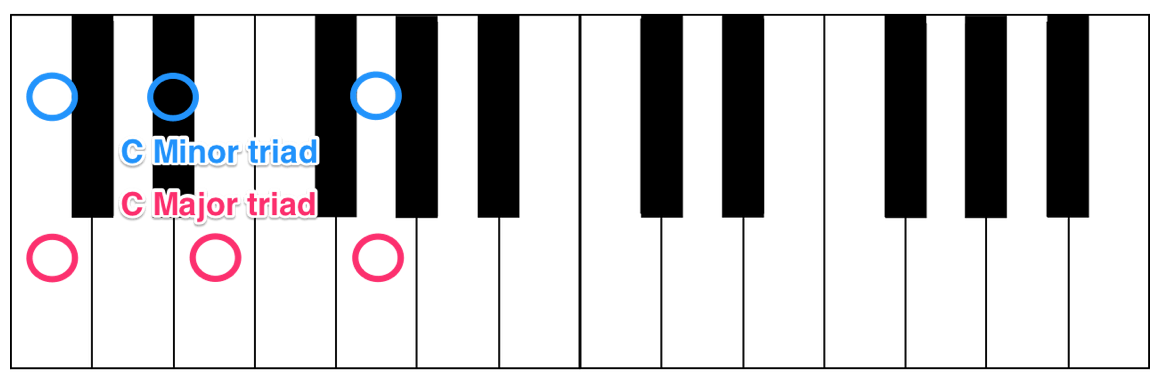
Major vs. Minor
While we’re at it, the distinction between major and minor chords is important to understand. Take a look at the major and minor scales below.

Major triad
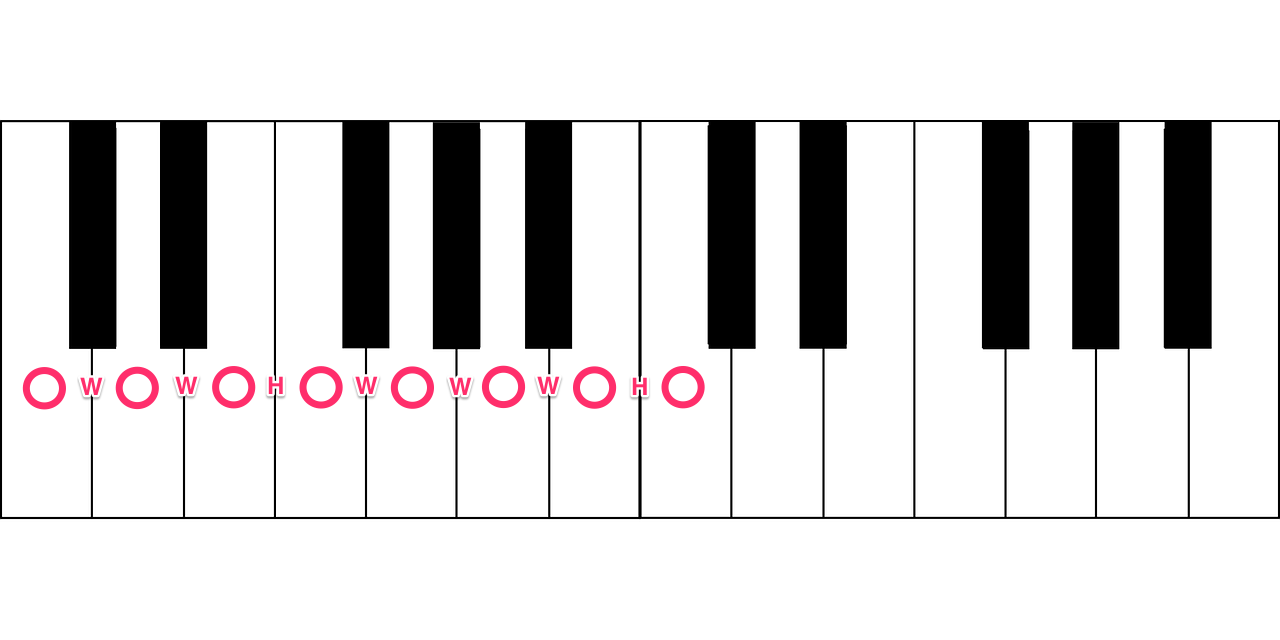
Major triad
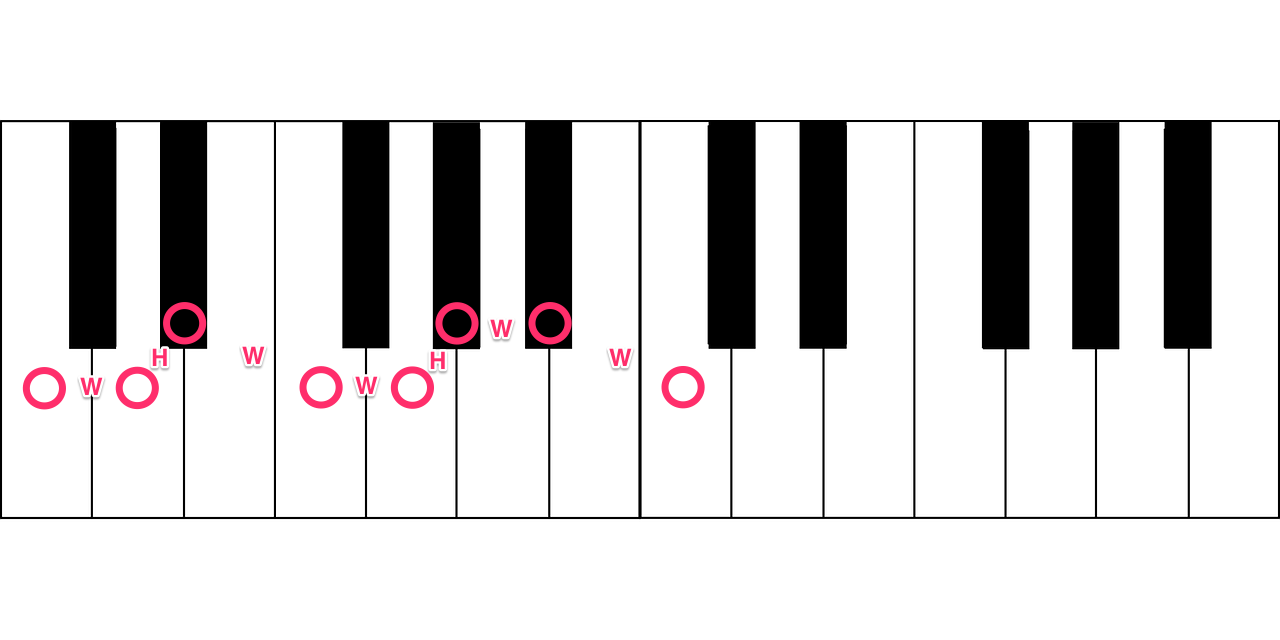
Major vs. minor scale comparison
Notice that the third note is different in the two scales. This note is a half step lower in the minor scale than it is in the major scale. Building a triad starting on the first note of each scale would create one starting with a major third and one with a minor third.
These chords, as you could expect, are called a major and minor triad, specifically a C Major triad (or just C Major) and a C Minor triad (or just C Minor).
Major & minor triads
Learn more about Basic Music Theory in part 2 of this article.


